B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the risk-free rate, rRF, increases but the market risk premium, (rM − rRF) , declines, with the net effect being that the overall required return on the market, rM, remains constant. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The required return will decline for stocks that have a beta less than 1.0 but will increase for stocks that have a beta greater than 1.0.
B) Since the overall return on the market stays constant, the required return on each individual stock will also remain constant.
C) The required return will increase for stocks that have a beta less than 1.0 but decline for stocks that have a beta greater than 1.0.
D) The required return of all stocks will fall by the amount of the decline in the market risk premium.
E) The required return of all stocks will increase by the amount of the increase in the risk-free rate.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely to be true for a portfolio of 40 randomly selected stocks?
A) The riskiness of the portfolio is the same as the riskiness of each stock if it was held in isolation.
B) The beta of the portfolio is less than the average of the betas of the individual stocks.
C) The beta of the portfolio is equal to the average of the betas of the individual stocks.
D) The beta of the portfolio is larger than the average of the betas of the individual stocks.
E) The riskiness of the portfolio is greater than the riskiness of each of the stocks if each was held in isolation.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following information for three stocks, A, B, and C. The stocks' returns are positively but not perfectly positively correlated with one another, i.e., the correlations are all between 0 and 1. Portfolio AB has half of its funds invested in Stock A and half in Stock B. Portfolio ABC has one third of its funds invested in each of the three stocks. The risk-free rate is 5%, and the market is in equilibrium, so required returns equal expected returns. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
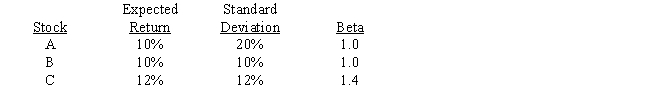
A) Portfolio AB's coefficient of variation is greater than 2.0.
B) Portfolio AB's required return is greater than the required return on Stock A.
C) Portfolio ABC's expected return is 10.66667%.
D) Portfolio ABC has a standard deviation of 20%.
E) Portfolio AB has a standard deviation of 20%.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A stock with a beta equal to −1.0 has zero systematic (or market) risk.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the market is in equilibrium and that Portfolio AB has 50% invested in Stock A and 50% invested in Stock B. Stock A has an expected return of 10% and a standard deviation of 20%. Stock B has an expected return of 13% and a standard deviation of 30%. The risk-free rate is 5% and the market risk premium, rM − rRF, is 6%. The returns of Stock A and Stock B are independent of one another, i.e., the correlation coefficient between them is zero. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since the two stocks have zero correlation, Portfolio AB is riskless.
B) Stock B's beta is 1.0000.
C) Portfolio AB's required return is 11%.
D) Portfolio AB's standard deviation is 25%.
E) Stock A's beta is 0.8333.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Data for Atwill Corporation is shown below. Now Atwill acquires some risky assets that cause its beta to increase by 30%. In addition, expected inflation increases by 2.00%. What is the stock's new required rate of return? Initial beta 1) 00 Initial required return (rs) 10) 20% Market risk premium, RPM 6) 00% Percentage increase in beta 30) 00% Increase in inflation premium, IP 2) 00%
A) 14.00%
B) 14.70%
C) 15.44%
D) 16.21%
E) 17.02%
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If you plotted the returns on a given stock against those of the market, and if you found that the slope of the regression line was negative, the CAPM would indicate that the required rate of return on the stock should be greater than the risk-free rate for a well-diversified investor, assuming that the observed relationship is expected to continue into the future.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stock A's beta is 1.7 and Stock B's beta is 0.7. Which of the following statements must be true about these securities? (Assume market equilibrium.)
A) Stock B must be a more desirable addition to a portfolio than A.
B) Stock A must be a more desirable addition to a portfolio than B.
C) The expected return on Stock A should be greater than that on B.
D) The expected return on Stock B should be greater than that on A.
E) When held in isolation, Stock A has more risk than Stock B.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stock A's beta is 1.7 and Stock B's beta is 0.7. Which of the following statements must be true, assuming the CAPM is correct.
A) In equilibrium, the expected return on Stock B will be greater than that on Stock A.
B) When held in isolation, Stock A has more risk than Stock B.
C) Stock B would be a more desirable addition to a portfolio than A.
D) In equilibrium, the expected return on Stock A will be greater than that on B.
E) Stock A would be a more desirable addition to a portfolio then Stock B.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Brodkey Shoes has a beta of 1.30, the T-bill rate is 3.00%, and the T-bond rate is 6.5%. The annual return on the stock market during the past 3 years was 15.00%, but investors expect the annual future stock market return to be 13.00%. Based on the SML, what is the firm's required return?
A) 13.51%
B) 13.86%
C) 14.21%
D) 14.58%
E) 14.95%
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Barker Corp. has a beta of 1.10, the real risk-free rate is 2.00%, investors expect a 3.00% future inflation rate, and the market risk premium is 4.70%. What is Barker's required rate of return?
A) 9.43%
B) 9.67%
C) 9.92%
D) 10.17%
E) 10.42%
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Diversification will normally reduce the riskiness of a portfolio of stocks.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Logically, it is easier to estimate the betas associated with capital budgeting projects than the betas associated with stocks, especially if the projects are closely associated with research and development activities.
B) The beta of an "average stock," which is also "the market beta," can change over time, sometimes drastically.
C) If a newly issued stock does not have a past history that can be used for calculating beta, then we should always estimate that its beta will turn out to be 1.0. This is especially true if the company finances with more debt than the average firm.
D) During a period when a company is undergoing a change such as increasing its use of leverage or taking on riskier projects, the calculated historical beta may be drastically different from the beta that will exist in the future.
E) If a company with a high beta merges with a low-beta company, the best estimate of the new merged company's beta is 1.0.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the risk-free rate is 5%. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If a stock's beta doubled, its required return under the CAPM would also double.
B) If a stock's beta doubled, its required return under the CAPM would more than double.
C) If a stock's beta were 1.0, its required return under the CAPM would be 5%.
D) If a stock's beta were less than 1.0, its required return under the CAPM would be less than 5%.
E) If a stock has a negative beta, its required return under the CAPM would be less than 5%.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stock A has an expected return of 12%, a beta of 1.2, and a standard deviation of 20%. Stock B also has a beta of 1.2, but its expected return is 10% and its standard deviation is 15%. Portfolio AB has $300,000 invested in Stock A and $100,000 invested in Stock B. The correlation between the two stocks' returns is zero (that is, rA,B = 0) . Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The stocks are not in equilibrium based on the CAPM; if A is valued correctly, then B is overvalued.
B) The stocks are not in equilibrium based on the CAPM; if A is valued correctly, then B is undervalued.
C) Portfolio AB's expected return is 11.0%.
D) Portfolio AB's beta is less than 1.2.
E) Portfolio AB's standard deviation is 17.5%.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a stock's market price exceeds its intrinsic value as seen by the marginal investor, then the investor will sell the stock until its price has fallen down to the level of the investor's estimate of the intrinsic value.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The risk-free rate is 6%; Stock A has a beta of 1.0; Stock B has a beta of 2.0; and the market risk premium, rM − rRF, is positive. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Stock B's required rate of return is twice that of Stock A.
B) If Stock A's required return is 11%, then the market risk premium is 5%.
C) If Stock B's required return is 11%, then the market risk premium is 5%.
D) If the risk-free rate remains constant but the market risk premium increases, Stock A's required return will increase by more than Stock B's.
E) If the risk-free rate increases but the market risk premium stays unchanged, Stock B's required return will increase by more than Stock A's.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The slope of the SML is determined by investors' aversion to risk. The greater the average investor's risk aversion, the steeper the SML.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the risk-free rate remains constant, but the market risk premium declines. Which of the following is most likely to occur?
A) The required return on a stock with beta > 1.0 will increase.
B) The return on "the market" will remain constant.
C) The return on "the market" will increase.
D) The required return on a stock with beta < 1.0 will decline.
E) The required return on a stock with beta = 1.0 will not change.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 146
Related Exams