A) The slow step in an SN1 mechanism is the dissociation step, which produces a carbanion and a leaving group.
B) In an SN1 mechanism, during the second step the nucleophile attacks the carbocation formed in the first step.
C) Primary alkylhalides are the best substrates for SN1 reactions.
D) The hydroxyl (OH-) group is an excellent leaving group in SN1 reactions.
E) During SN1 reactions the absolute configuration of the substrate is retained in the product.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Give the organic product for the following reaction. CH3CH2CH2NH2 + HCl
A) ClCH2CH2CH2NH2
B) CH3CHClCH2NH2
C) CH3CH2CHClNH2
D) CH3CH2CH2NHCl
E) CH3CH2CH2NH3+Cl-
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the balanced chemical equation for the catalytic hydrogenation (addition of H2) to CH3CH=CHCH3?
A) CH3CH=CHCH3 + 2H2 → 2CH3CH3
B) CH3CH=CHCH3 + 3H2 → CH3CH3 + 2 CH4
C) CH3CH=CHCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH3 + CH4
D) CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH3
E) CH3CH=CHCH3 + 4H2 → 4CH4
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the product obtained after a reaction between an aldehyde and Grignard reagent is worked-up with dilute acid?
A) a ketone
B) a primary alcohol
C) a secondary alcohol
D) a tertiary alcohol
E) a carboxylic acid
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) In nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom, a carbon with a positive charge behaves as a nucleophile.
B) Nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom can follow one of three mechanisms: SN1, SN2, and SN3.
C) A carbon atom with a partial positive charge can react with a nucleophile, a molecule, or ion that has a lone pair of electrons.
D) Alkanes are an example of saturated organic compounds that easily participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom.
E) In nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom, the replaced group is called an electrophile.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents the addition polymer formed from the compound below? CH2=CHCl
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -strong base
A) substitution at saturated carbon atom, mechanism
B) LiAlH4
C) H+
D) step-growth
E) elimination reaction mechanism
F) Jones reagent
G) hemiketal
H) methoxide
I) CN-
K) E) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the weak acid from the compounds below.
A) CH3CH2NH2
B) CH3CH2CO2H
C) CH3CH2OCH3
D) CH3CH2F
E) CH3COOC2H5
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The nucleophile strongly influences both SN1 and SN2 reactions, while the nature of the nucleophile and the substrate structure are only important in SN2 reactions.
B) The structure of the substrate is the only important factor for SN1 reactions, while the nucleophile, leaving group, and the structure of the substrate are all important for SN2 reactions.
C) For SN2 reactions the only important factor to consider is the leaving group; for SN1 reactions the structure of the substrate and the nature of the nucleophile are the most important factors.
D) The nucleophile and leaving group are both important in SN2 reactions, while for the SN1 reactions the leaving group and the structure of the substrate are very significant.
E) The nucleophile is not important for SN2 reactions, but the structure of the substrate is very important; for SN1 reactions the opposite is true.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) During the electrophilic aromatic substitutions, the resonance stabilized carbocation reacts with a base to give the addition product.
B) Aromatic compounds are very reactive because they contain more than one C=C double bond in their structure.
C) The rate-determining (slow) step of electrophilic aromatic substitutions is the deprotonation of the carbocation intermediate.
D) Unlike alkenes, aromatic compounds almost always prefer electrophilic substitution over electrophilic addition.
E) During the electrophilic aromatic substitution a Bronsted or Lewis acid is required to generate the nucleophile from an aromatic substrate.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -oxidizing agent
A) substitution at saturated carbon atom, mechanism
B) LiAlH4
C) H+
D) step-growth
E) elimination reaction mechanism
F) Jones reagent
G) hemiketal
H) methoxide
I) CN-
K) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Elimination reactions take place with the retention of the absolute configuration.
B) The most common substrates in elimination reactions are ketones and amines.
C) A dehydration reaction produces an alkane and one equivalent of water.
D) The major product in an elimination reaction is the less substituted alkene.
E) A dehydrohalogenation reaction requires the presence of a strong base and heat.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -E2
A) substitution at saturated carbon atom, mechanism
B) LiAlH4
C) H+
D) step-growth
E) elimination reaction mechanism
F) Jones reagent
G) hemiketal
H) methoxide
I) CN-
K) B) and I)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the product obtained from the reaction between a ketone and a primary alcohol?
A) a secondary alcohol
B) a tertiary alcohol
C) a hemiacetal
D) a hemiketal
E) a carboxylic acid
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the product of the following reaction: 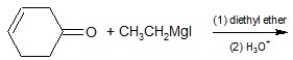
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -SN1
A) substitution at saturated carbon atom, mechanism
B) LiAlH4
C) H+
D) step-growth
E) elimination reaction mechanism
F) Jones reagent
G) hemiketal
H) methoxide
I) CN-
K) F) and I)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of polymers are polyesters?
A) Polyesters, formed via step-growth polymerization of diacids and diols, have the monomers connected through ester groups.
B) Polyesters, formed via step-growth polymerization of acids and diols, have the monomers connected through ester groups.
C) Polyesters, formed via step-growth polymerization of acids and alcohols, have the monomers connected through ester groups.
D) Polyesters, formed via addition polymerization of diacids and diols, have the monomers connected through ester groups.
E) Polyesters, formed via step-growth polymerization of diacids and diols, have the monomers connected via hydrogen bonds.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the product(s) of the reduction of the following compound: 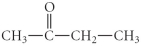
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write a balanced chemical reaction to represent the combustion of 2,2-dimethylpropane.
A) C5H12 + 8O2 → 5CO2 + 6H2O
B) C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
C) C5H12 + H2 → CH4 + 2C2H6
D) C3H8 + H2 → CH4 + C2H6
E) 2 C3H8 + O2 → 3CH4 + 2H2O
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the products of the following reaction: 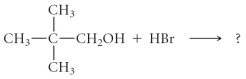
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 96
Related Exams