A) If the N/Z ratio is too high, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will convert a neutron to a proton via beta decay.
B) If the N/Z ratio lies somewhere below 1, the nuclide is stable.
C) If the N/Z ratio is too low, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will undergo beta decay.
D) The valley of stability is the geographic location where many of the known nuclides were first discovered.
E) All stable nuclei have an N/Z ratio equal to 1.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If we start with 1.000 g of cobalt-60, 0.675 g will remain after 3.00 y. This means that the half-life of cobalt-60 is ________ y.
A) 3.08
B) 4.44
C) 2.03
D) 5.29
E) 7.65
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Describe what changes occur in the atomic nucleus during alpha decay.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Above what atomic number are there no stable isotopes of any element?
A) 20
B) 92
C) 83
D) 40
E) 89
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear equation: 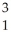 H +
H + 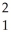 H ?
H ? 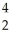 He + ? +
He + ? + 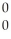 g
g
A) ![]() e
e
B) ![]() n
n
C) ![]() e
e
D) ![]() H
H
E) ![]()
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 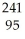 Am →
Am → 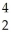 He +
He + 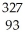 Np
Np
A) beta emission
B) neutron bombardment
C) alpha emission
D) electron capture
E) positron emission
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the mass defect in Fe-56 if the mass of an Fe-56 nucleus is 55.921 amu. The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and the mass of a neutron is 1.008665 amu.
A) 0.528 amu
B) 3.507 amu
C) 0.564 amu
D) 1.056 amu
E) 0.079 amu
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by 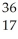 Cl.
Cl.
A) ![]() Ar
Ar
B) ![]() K
K
C) ![]() S
S
D) ![]() P
P
E) ![]() Ar
Ar
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the beta decay of 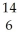 C.
C.
A) ![]() N
N
B) ![]() Be
Be
C) ![]() N
N
D) ![]() C
C
E) ![]() B
B
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stable isotopes with low atomic numbers have an N/Z ratio of 1. What does that imply?
A) The number of neutrons equals the number of protons.
B) The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons plus protons.
C) The number of protons equals the number of electrons.
D) The atomic number equals the atomic mass.
E) The number of protons equals the number of electrons plus neutrons.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
positron Match the following.
A) ![]() e
e
B) ![]() He
He
C) ![]() e
e
D) ![]()
E) ![]() p
p
F) ![]() n
n
H) E) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following equations shows the correct relationship between the half-cell of a nuclide and the radioactive decay rate constant?
A) ln ![]() = -
= - ![]()
B) ![]() = - ln
= - ln ![]()
C) ![]() = 0.693 × k
= 0.693 × k
D) ![]() =
= ![]()
E) ![]() =
= ![]()
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The splitting of the uranium atom is called ________.
A) radioactive cleavage
B) nuclear fission
C) nuclear fusion
D) radioactive merge
E) the half-life
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nuclides above the valley of stability can become more stable through which of the following processes?
A) beta emission
B) positron emission
C) gamma emission
D) electron capture
E) neutron bombardment
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via beta decay?
A) I-126
B) Al-24
C) N-13
D) Cs-137
E) Na-20
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete the following equation of transmutation. 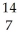 N +
N + 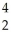 He ?
He ? 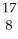 O + ______
O + ______
A) ![]() e
e
B) ![]()
C) ![]() e
e
D) ![]() H
H
E) ![]() n
n
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the symptom experienced from radiation exposure.
A) increased ability to absorb nutrients
B) sneezing
C) death
D) decreased risk of cancer
E) weaker immune system
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following nuclides is most likely to undergo beta decay?
A) ![]() Pt
Pt
B) ![]() Pt
Pt
C) ![]() Pt
Pt
D) ![]() Pt
Pt
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 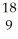 F.
F.
A) ![]() Na
Na
B) ![]() F
F
C) ![]() N
N
D) ![]() O
O
E) ![]() Ne
Ne
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Potassium-40 decays to argon-40 with a half-life of 1.27 × 109 yr. The age of a mineral sample that has a mass ratio of 40Ar to 40K of 0.812 is ________ y.
A) 1.56 × 109
B) 1.02 × 109
C) 1.47 × 109
D) 7.55 × 108
E) 1.09 × 109
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 115
Related Exams