A) cartilage
B) collagen fibers
C) capsules
D) synovial membranes
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Joints are classified according to the
A) bones that are united at the joint.
B) structure of the joint.
C) size of the joint.
D) shape of the joint.
E) type of fluid in the joint.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bowing the head is an example of ________.
A) rotation
B) pronation
C) flexion
D) lateral excursion
E) hyperextension
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The glenoid labrum is part of the ________ joint, while the acetabular labrum is part of the ________ joint.
A) elbow; knee
B) shoulder; hip
C) shoulder; knee
D) elbow; hip
E) shoulder; elbow
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mary Lu is experiencing pain from her sacroiliac joint. In what region of her body is she most likely feeling pain?
A) Posterior pelvic region
B) Anterior pelvic region
C) Cervical region
D) Lumbar region
E) Thoracic region
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most of the joints in the appendicular skeleton are ________ joints.
A) fibrous
B) immovable
C) synovial
D) cartilaginous
E) inarticulate
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following joints is most movable?
A) Plane
B) Saddle
C) Hinge
D) Pivot
E) Ball and socket
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
LaTonya gets her hand caught in the car door at her knuckles. Which of these specific joints is injured?
A) Radiocarpal joint
B) Metacarpophalangeal joint
C) Atlantoaxial joint
D) Metatarsophalangeal joint
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A joint that has no joint cavity and exhibits little or no movement would be classified as a ________ joint.
A) fibrous
B) synovial
C) complex
D) cartilaginous
E) partial
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The simplest types of movement at a synovial joint are ________ movements.
A) angular
B) circular
C) fibrous
D) gliding
E) special
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The joint between the head of the radius and the proximal end of the ulna is a ________ joint.
A) plane
B) saddle
C) hinge
D) pivot
E) ball and socket
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
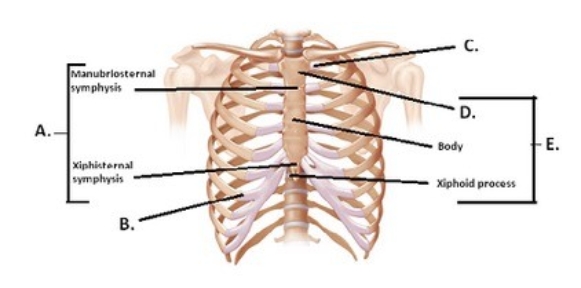 -The figure illustrates the joints and bones of the rib cage. What does "D" represent?
-The figure illustrates the joints and bones of the rib cage. What does "D" represent?
A) Costochondral joint
B) Sternum
C) Manubrium
D) Sternal symphyses
E) Sternocostal synchrondrosis
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A place where two or more bones come together is a/an ________.
A) cavity
B) joint
C) contusion
D) articulation
E) Both "joint" and "articulation" are correct.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lyme disease is
A) a bacterial infection transmitted by ticks.
B) an inflammation of any joint.
C) a metabolic disorder caused by increased uric acid in blood.
D) a condition that may involve an autoimmune disease.
E) the most common type of arthritis.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Joints joined together by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage would be classified as ________ joints.
A) cartilaginous
B) fibrous
C) synovial
D) diarthrotic
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ellipsoid joints
A) are multiaxial joints.
B) are found between adjacent vertebra.
C) are actually modified ball and socket joints.
D) allow free rotation.
E) are modified pivot joints.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures prevents knee hyperextension?
A) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
B) The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
C) The fibular (lateral) collateral ligament
D) The medial meniscus
E) The lateral meniscus
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
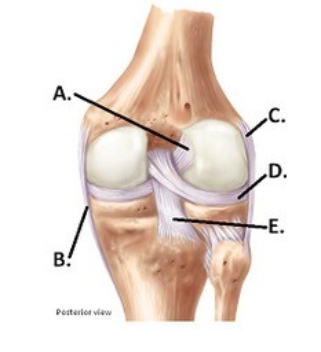 -The figure illustrates a posterior view of the right knee joint. What does "E" represent?
-The figure illustrates a posterior view of the right knee joint. What does "E" represent?
A) Medial (tibial) collateral ligament (MCL)
B) Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
C) Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
D) Lateral (fibular) collateral ligament (LCL)
E) Lateral meniscus
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A biaxial joint has movement
A) around one axis.
B) around two axes at right angles to one another.
C) about several axes.
D) as long as there is articular cartilage present.
E) that always rotates.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an effect of aging on the joints?
A) Decreased range of motion
B) Decreased flexibility and elasticity
C) Increased production of synovial fluid
D) Weakening of muscles
E) Decreased tissue repair
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 149
Related Exams